How Much of the World’s Energy Comes from Coal in Total?
Is coal still a major player in powering our world? The answer, unfortunately, is yes. Understandinghow muchof the world’s energy comes from coal is crucial for grasping the scope of the climate challenge and the transition to cleaner energy sources. Coal remains a significant contributor to global electricity generation and industrial processes, despite growing concerns about its environmental impact. This article explores the current percentage of global energy derived from coal, the factors driving its continued use, and the implications for the future of energy. We will delve into the global energy mix, focusing on coal's contribution, its historical trends, regional variations, and the ongoing efforts to reduce reliance on this carbon-intensive fuel.
All About How Much of the World’s Energy Comes from Coal in Total?
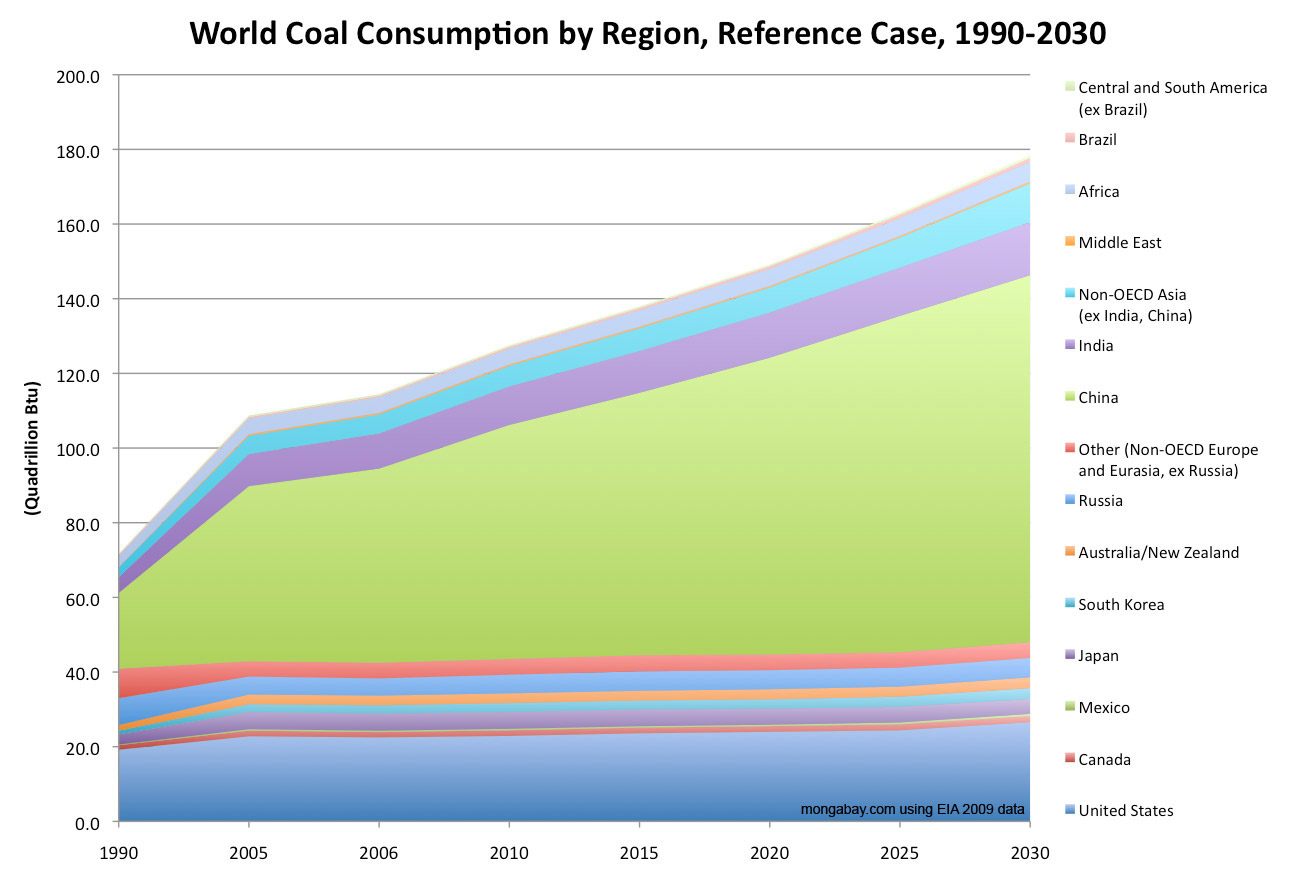
The percentage of the world’s energy derived from coal fluctuates, but in recent years, it has consistently accounted for a substantial portion. Coal, a fossil fuel formed from decayed plant matter over millions of years, is primarily used for electricity generation and industrial applications, such as steel production and cement manufacturing. Its continued significance stems from its abundance, affordability (in some regions), and established infrastructure.
Defining Coal's Contribution: To accurately quantifyhow muchof the world’s energy supply relies on coal, we must consider its share in the total primary energy supply (TPES). TPES encompasses all energy sources consumed by a country or region, including coal, oil, natural gas, nuclear, renewables, and other sources. Various sources, like the International Energy Agency (IEA) and BP Statistical Review of World Energy, provide data on TPES, allowing us to calculate the percentage attributable to coal. These statistics allow us to analyze the overall benefits and detriments of using coal as an energy source.
Historical Con The use of coal as a major energy source dates back to the Industrial Revolution. The availability and affordability of coal compared to other energy sources made it the cornerstone of energy production in various countries. Over time, the prominence of coal has changed due to technological advancements, energy policies, and environmental concerns.
Unique Features and Usage: While renewable energy and natural gas use is growing, coal usage is still very prominent in countries with large industrial sectors or developing economies. Coal is most widely used for the following: Electricity Generation: A primary use of coal is in power plants, where it is burned to heat water, create steam, and turn turbines connected to generators. Steel Production: Coal is converted to coke, a vital ingredient in blast furnaces for steel manufacturing. Cement Manufacturing: The high temperatures required for cement production are often achieved by burning coal.
Expert Opinion: According to Dr. Emily Carter, a professor of energy and environmental engineering, "Coal continues to play a significant role in the global energy mix, particularly in developing economies where access to affordable energy is paramount. However, the environmental costs associated with coal combustion are undeniable. The challenge lies in transitioning to cleaner energy sources while ensuring energy security and affordability."
Benefits of How Much of the World’s Energy Comes from Coal for Users
While the direct benefits to individual users may not be immediately apparent, the indirect benefits of coal in terms of affordable energy and industrial production have played a significant role in shaping modern society. It's important to acknowledge these benefits while also recognizing the imperative to transition to more sustainable alternatives.
Affordable Energy Access: In certain regions, coal provides a relatively inexpensive source of energy, making electricity more accessible to a wider population. This can improve living standards, facilitate economic development, and enhance educational opportunities. Coal also ensuresenergy securitywithin various regions.
Industrial Development: Industries heavily rely on coal for energy and manufacturing purposes. The availability of coal can support industrial growth, leading to job creation and economic prosperity.
Comparison with Alternatives: Compared to some renewable energy sources, coal-fired power plants are reliable and can provide a continuous base load of electricity. This contrasts with the intermittent nature of solar and wind power, which require energy storage solutions or backup generation.
Data and Research: According to a report by the World Coal Association, coal-fired power plants provide a significant percentage of electricity in many countries, including China and India. These countries rely on coal to meet their growing energy demands, supporting industrial growth and providing power to millions of homes and businesses.
How to Reduce The Usage of Coal
Reducing coal usage andhow toimplement these steps can be achieved through a combination of policy measures, technological advancements, and changes in consumer behavior.
1. Investing in Renewable Energy Sources
To lessen thebenefits ofcoal, it is important to invest in renewable energy sources. Investing heavily in renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, hydro, and geothermal can provide cleaner and more sustainable alternatives to coal-fired power generation. This transition requires supportive government policies, financial incentives, and technological advancements to improve the efficiency and reliability of renewable energy systems.
2. Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Implementing energy-efficient technologies and practices in buildings, industries, and transportation can reduce overall energy demand and, consequently, the need for coal-fired power. Energy efficiency measures include improved insulation, efficient lighting, smart grids, and electric vehicles.
3. Carbon Capture and Storage (CCS)
Implementing carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies at coal-fired power plants can help mitigate carbon emissions by capturing CO2 from flue gases and storing it underground or in other geological formations. While CCS technology is still under development and deployment, it holds promise for reducing the carbon footprint of coal power.
4. Implementing Carbon Pricing Mechanisms
Introducing carbon pricing mechanisms, such as carbon taxes or cap-and-trade systems, can incentivize companies and individuals to reduce their carbon emissions by making them pay for the environmental costs associated with burning coal. This can encourage investment in cleaner energy sources and promote energy efficiency.
Tips Before Using How Much of the World’s Energy Comes from Coal
Before making decisions based on the percentage of energy from coal, consider the following: Consider Data Sources: Always rely on reputable sources like the IEA, BP, and government energy agencies for accurate data on coal consumption and energy mix. Understand Regional Variations: Recognize that coal reliance varies significantly by region. Factors like resource availability, economic development, and energy policies influence coal usage. Stay Informed: Keep up-to-date with the latest trends and developments in the energy sector, including the adoption of renewable energy technologies and policy changes related to coal. Assess the Con Evaluate the percentage of energy from coal in the context of broader energy and climate goals. Consider the environmental impact and the potential for transitioning to cleaner alternatives.
Common Issues and Solutions Related to How Much of the World’s Energy Comes from Coal
Several issues are associated withhow muchof the world relies on coal: Environmental Impact:Coal combustion releases greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change and air pollution, which is a detriment for thesolutions forthe globe's overall health.
Solution: Implementing stringent emission standards and investing in pollution control technologies can mitigate the environmental impact of coal-fired power plants. Economic Dependence: Some regions are heavily dependent on coal mining and coal-fired power generation, making it difficult to transition to cleaner energy sources.
Solution: Providing financial assistance, retraining programs, and economic diversification initiatives can help coal-dependent communities transition to new industries. Energy Security: In some countries, coal provides a reliable and affordable source of energy, ensuring energy security and reducing dependence on imported fuels.
Solution: Diversifying the energy mix with a combination of renewable energy sources, natural gas, and nuclear power can enhance energy security while reducing reliance on coal.
Conclusion
Despite the growing momentum towards cleaner energy sources, coal continues to be a significant contributor to the global energy mix, driven by its affordability, availability, and existing infrastructure. Reducinghow muchthe world relies on coal requires a multifaceted approach that encompasses investment in renewable energy, enhanced energy efficiency, carbon capture and storage, and supportive policy measures. Transitioning to a cleaner energy future is essential for mitigating climate change and ensuring a sustainable future. By understanding the challenges and opportunities associated with coal, we can work towards a more sustainable and resilient energy system that benefits both the environment and society. It's important to be informed on how thebenefits ofrenewable sources can impact our reliance on coal. As technology continues to advance and policies evolve, we can expect to see further progress in reducing reliance on coal and transitioning to a cleaner energy future.

Posting Komentar untuk "How Much of the World’s Energy Comes from Coal in Total?"