Where Does Coal Energy Come From and How Is It Formed?
Have you ever wondered where the energy powering our homes and industries truly begins? The answer lies deep beneath our feet, in a substance we often take for granted: coal. This blog post delves into the fascinating origin story of coal, exploring how it's formed over millions of years and revealing the incredible journey from ancient plant life to a valuable energy source. Understanding the formation of coal helps us appreciate both its potential and the environmental considerations associated with its use. Join us as we uncover the secrets behind this fossil fuel, exploring the geological processes, different types of coal, and the impact its use has on our planet.
All About Where Does Coal Energy Come From and How Is It Formed?
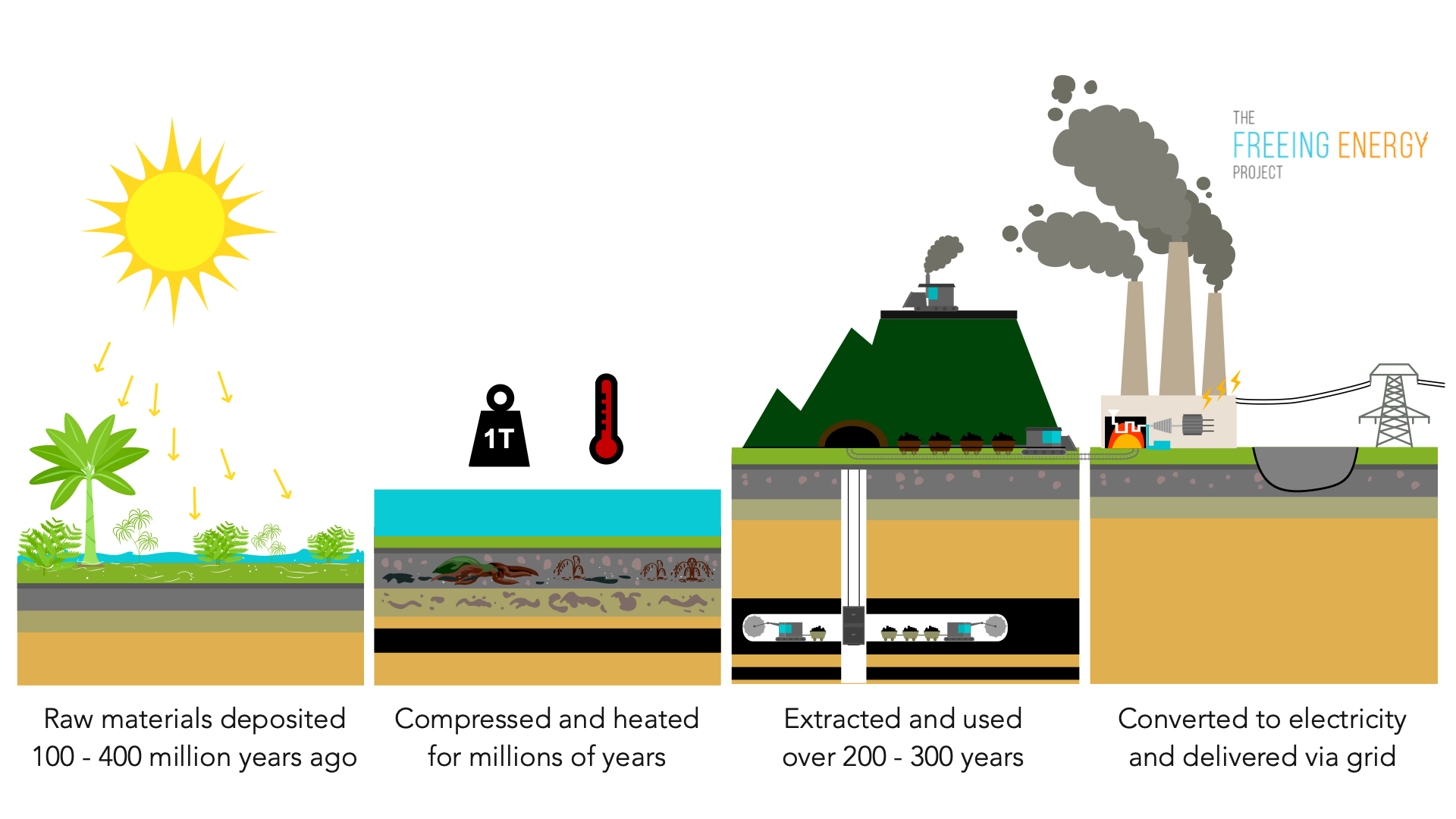
Coal energy is fundamentally derived from thestored solar energycaptured by plants millions of years ago. The coal formation process, known ascoalification, is a long and complex transformation of plant matter into a carbon-rich substance through a series of geological and biochemical processes. This process typically takes place in swampy environments where dead plant material accumulates faster than it decomposes. Understanding this process is crucial to grasping the significance of coal as afossil fueland its role in energy production. Coal’s significance lies in its abundance and historical role as a relatively inexpensive source of energy. It has powered industrial revolutions and continues to contribute significantly to global electricity generation.
The story of coal begins hundreds of millions of years ago, during the Carboniferous period (approximately 360 to 300 million years ago). This era was characterized by warm, humid climates and vast, swampy forests dominated by giant ferns, club mosses, and horsetails. These plants, unlike their modern counterparts, contained significant amounts of lignin, a complex polymer that is difficult for microorganisms to decompose. As these plants died, they accumulated in the swampy environments, forming thick layers of peat. Over time, this peat became buried under layers of sediment and subjected to increasing pressure and temperature. This is where the transformation begins.
What differentiates coal from other resources is itsunique carbon content. Through the coalification process, coal goes through various stages, each characterized by increasing carbon content and energy density. These stages include peat, lignite, bituminous coal, and anthracite. Each stage represents a further degree of compaction and carbon concentration. The higher the carbon content, the greater the energy released when the coal is burned.
Expert geologists emphasize the importance of understanding the geological context in which coal forms. The specific conditions, such as the type of vegetation, the rate of sedimentation, and the temperature and pressure, all influence the type and quality of coal that is formed. Therefore, the geological history of a region plays a critical role in determining the presence and characteristics of its coal deposits.
Benefits of Coal Energy for Users
While the environmental impact of coal use is a significant concern, it’s important to acknowledge the benefits it has provided to users throughout history and continues to provide today. Coal provides areliable and relatively inexpensivesource of energy for electricity generation, powering homes, businesses, and industries. This reliability is particularly important in regions where renewable energy sources may be intermittent.
Historically, the accessibility and affordability of coal made it a driving force behind the Industrial Revolution, fueling the steam engines that powered factories and transportation systems. Today, coal-fired power plants remain a significant source of electricity in many countries, especially in developing nations where it can be a more accessible and affordable option compared to other energy sources. Coal's importance also extends to steel production.Coking coalis essential in the process of making steel, which is a fundamental material in construction, manufacturing, and infrastructure development.
Compared to some renewable energy sources, coal-fired power plants can provide aconsistent and predictableoutput of electricity, helping to maintain grid stability. However, it is essential to note that advancements in renewable energy technologies and energy storage solutions are increasingly challenging this advantage. Furthermore, the environmental costs associated with coal extraction and combustion need to be carefully considered when comparing it to alternative technologies. While advancements inclean coal technologiesaim to reduce emissions, they are not yet widely implemented and do not eliminate the overall environmental impact.
Research suggests that while coal has been a vital resource, its long-term use presents significant environmental challenges. Studies consistently highlight the link between coal combustion and air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and other environmental problems. This underscores the importance of transitioning towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources.
How to Use Coal Energy
Using coal energy isn't something most individuals directly "use" in the way they use solar panels or natural gas. Instead, it's the energy generatedfromcoal that powers homes and industries. However, understanding the process is important.
1. Extraction and Processing
The first step involves extracting coal from the earth, typically throughsurface mining(also known as strip mining) orunderground mining. Surface mining is used when coal seams are close to the surface, while underground mining is employed when the coal is deeper down. Once extracted, the coal is processed to remove impurities and increase its heating value. This can involve crushing, washing, and sorting the coal. Best practices involve minimizing the environmental impact of mining operations through land reclamation and water treatment.
2. Combustion
The processed coal is then burned in apower plantto heat water and produce steam. This steam drives turbines connected to generators, which convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. Modern power plants employ advanced technologies to improve efficiency and reduce emissions. Optimization tips include maintaining optimal combustion conditions and using flue gas desulfurization to remove sulfur dioxide.
3. Electricity Transmission
The electricity generated is then transmitted through a network ofpower linesto homes, businesses, and industries. This involves transformers that step up the voltage for efficient transmission and then step it down again for distribution to end-users. Common mistakes to avoid include overloading the grid and neglecting maintenance of transmission infrastructure.
Tips Before Using Coal Energy
Because individual users do not directly handle coal, the "use" is about understanding the implications of relying on coal-generated power and making informed energy choices.
Before relying on coal-generated energy, consider the environmental impact and explorealternative energy optionsif possible. Support policies that promote cleaner energy sources and energy efficiency. Avoid contributing to excessive energy consumption and waste.
Ignoring these tips can contribute to increased air pollution, greenhouse gas emissions, and climate change. The consequences of continued reliance on coal without mitigation strategies are far-reaching and can impact future generations. Prioritizing energy conservation and supporting the development of renewable energy sources are essential for a sustainable future.
Common Issues and Solutions Related to Coal Energy
Potential issues with coal energy relate to environmental impacts and efficiency: Air Pollution: Coal combustion releases pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, which can cause respiratory problems and contribute to acid rain. Solutions include installing scrubbers and other pollution control equipment in power plants. Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Coal combustion is a major source of carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas that contributes to climate change. Solutions involve transitioning to cleaner energy sources, implementing carbon capture and storage technologies, and improving energy efficiency. Mining Environmental Impact: Coal mining can damage ecosystems, pollute waterways, and cause land subsidence. Solutions include implementing strict environmental regulations, reclaiming mined land, and using more sustainable mining practices. Efficiency: Older coal-fired power plants can be inefficient, wasting energy and increasing emissions. Solutions include upgrading power plants with more efficient technologies, such as supercritical and ultra-supercritical boilers.
Conclusion
Coal energy has played a pivotal role in powering human progress, from fueling the Industrial Revolution to providing electricity to homes and businesses today. However, understanding its origin, formation, and associated environmental impacts is crucial for making informed decisions about our energy future. By recognizing the benefits and drawbacks of coal energy, and supporting the development of cleaner alternatives, we can work towards a more sustainable and environmentally responsible energy system. Consider the tips provided for reducing your reliance on coal energy and advocating for cleaner energy policies. It's time to actively participate in shaping a future powered by innovation and sustainability.
Posting Komentar untuk "Where Does Coal Energy Come From and How Is It Formed?"